Human Reproductive System
1. Male Reproductive System
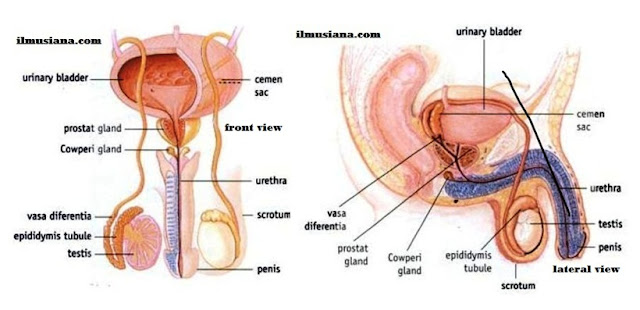
Testes
- Seminiferous tubules, a vast tangle of hollow tubules where spermatogenesis (the process of forming sperm) take place.
- Leydig cell, cells that produce man hormone (testosterone).
- Tuniva albuginea, testes coated layer.
Reproduction Duct
- Recti tubules, the place where seminiferus tubules exist. This tubules send the sperm to eferensia tubules.
- Eferensia tubule, a tubule that is used to collect sperm and send it to epididymis tubule.
- Epididymis tubules, a coiled tubule that has about 5 m long. There, sperms finish maturing and are stored. The base of epididymis is connected to vasa diferentia.
- Vasa diferentia (vas deferens), used to send sperms to urethra. In the end of vas deferens, there is a wider tubule that forms ampula. In this place, vasa diferentia meets tubule from semen sac (vesica seminalis). In semen sac, there is a releasing tubule which is so called ejaculation tubule. In ejaculation, semen fluid is sprout out to vagina through urethra in penis.
Addition Gland
- Semen sac (seminalis vesicle). Is used to collect semen that consists of fructose, ascorbic acid, and amino acid. These substances will be the nutrient for sperm. Semen is produced by gland cells ont the semen sac cell.
- Prostat gland, is placed on the lower end of urethra. This gland produces alkali milk-like fluid. This alkali is used to protect sperm from acidity of woman reproduction canal.
- Cowperi gland, (bulbourethra vesicle), placed on the tip of urethra after prostate gland. This gland has a function to produce mucus as smoothing liquid and add liquid to semen.
Penis
2. Woman Reproductive System
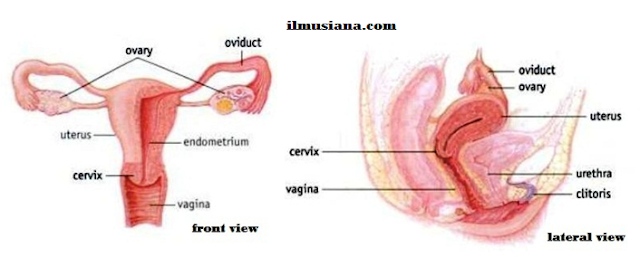
Ovary
Every woman has a couple of ovaries: the right and left ovaries. Ovary has two main functions: produce ovum and hormones. Ovum forming process is called oogenesis. Oogenesis occurs gradually and periodic, once a month. The moment when ovum left ovary is called ovulation. Hormones produced in ovary are estrogen and progesterone.Uterine Tube (Oviduct/Fallopian Tube)
Every woman has a couple of uterine tubes, right and left tubes that have about 12 cm long. In this tube fertilization occurs. At the base of uterine tube, there is a funnel-like structure to catch the ovum.Uterus
Uterus is the organ where embryo grows and develops to be a fetus that is ready to be born. Uterus has pear-like shape and thick walls. The wall is composed of three layers of tissue: outer tissue (cerose), middle tissue (myometrium), and inner tissue (endometrium).During ovum maturation, uterus wall will thicken. This wall thickening is prepared for embryo adhering (implantation) if fertilization happens. If fertilization does not occur during the monthly cycle, the wall sloughs off and is discharged in the process known as menstruation. Menstruation occurs periodically once a month.
Read: Excretory System Human BodyOvum forming process and menstruation occurs cyclically. There are four stages in for one cycle.
- Menstruation (day 1-7), releasing uterus wall because of decreasing sex hormone concentration in the body.
- Pre-ovulation (day 7-13), the time when ovum is produced and matured in the ovary. It was induced by increasing the body’s estrogen.
- Ovulation, the time when ovum is released from ovary. Ovulation usually occurs on 14th day of menstruation.
- Post-ovulation (day 15-28), the time of deterioration of ovum if feretilization does not occur. In this stage, progesterone production increases so endometrium thickens. Now, endometrium is ready to receive embryo that will develop. If fertilization does not occur, sex hormones will decrease so endometrium will be released.
Vagina
Vagina is woman copulation organ, the way for birth and the way for releasing endometrium when menstruation occurs.3. Sperm and Ovum
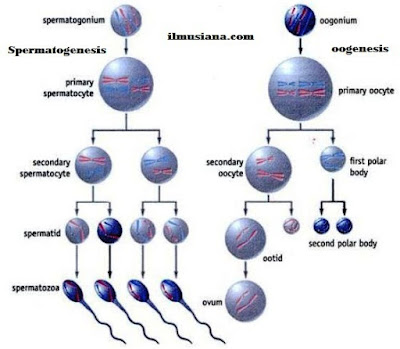
4. Fertilization and Embryo Development

- Supply nutrient and oxygen from mother to fetus.
- Discard waste from fetus to mother.
- Inhibit pathogen (diseases) and some dangerous chemical substances to enter the fetus body, and
- Give immune system from mother to fetus










0 komentar:
Post a Comment